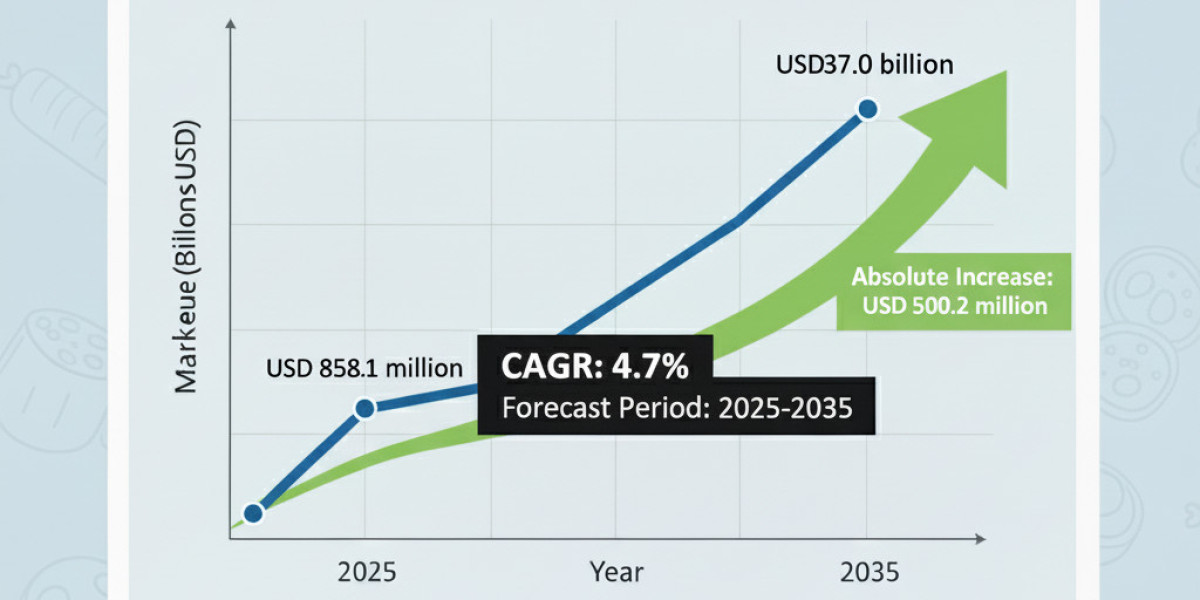
The global push toward clean energy is steering unprecedented attention toward renewable hydrogen technologies. As Per Market Research Future, the Green Hydrogen Market Outlook highlights how this sustainable fuel is becoming central to long-term decarbonization strategies across numerous industries seeking to replace fossil-based systems.
Green hydrogen, produced by splitting water using renewable electricity, stands out for its ability to integrate with diverse sectors such as mobility, manufacturing, chemicals, and power systems. Unlike conventional fuels, it generates no harmful emissions and provides a versatile, transportable, and high-density energy source. These advantages are driving wide adoption in applications where traditional electrification is difficult, enabling a foundational shift in how energy is stored, delivered, and consumed.
Market Trends and Strategic Developments
One dominant trend shaping the green hydrogen landscape is the intensifying alignment between government policy and industrial initiatives. Policy frameworks across regions are prioritizing renewable-based hydrogen production, creating incentives for infrastructure, manufacturing, and long-term research. This synergy is enhancing investor confidence and accelerating commercial-scale projects.
Technological progress also plays a pivotal role. Electrolyzer designs are evolving, becoming more efficient, modular, and adaptable for various climates and industrial requirements. New methods aim to reduce the cost of hydrogen production by optimizing materials and adopting innovative manufacturing techniques. As research advances, green hydrogen becomes increasingly competitive, appealing to both established energy players and emerging startup ecosystems.
Another defining trend is the rise of cross-sector partnerships. Energy providers, transportation agencies, industrial manufacturers, and research institutions are collaborating to build hydrogen hubs and supply chains. These partnerships ensure that hydrogen production aligns with demand centers, allowing seamless integration into existing infrastructure. Such cooperation not only lowers operational challenges but also ensures long-term stability of supply.
Applications Transforming the Global Energy Mix
Green hydrogen’s adaptability is leading to transformative applications. In transportation, it supports fuel cells for heavy mobility such as long-haul vehicles, marine transport, and aviation systems. These sectors require energy-dense fuels that can withstand long durations and demanding conditions, an area where hydrogen excels.
In industrial settings, hydrogen is facilitating clean processes in sectors like steel, fertilizers, and chemicals. Traditional production methods in these industries rely heavily on fossil sources, making green hydrogen an attractive alternative to reduce environmental footprints. The introduction of renewable hydrogen into industrial pathways marks a milestone in achieving cleaner manufacturing practices.
Energy storage is another critical application. With renewable electricity generation often fluctuating, green hydrogen serves as a reliable medium to store surplus energy from sources like solar and wind. This stored energy can be used when demand increases or supply decreases, supporting grid stability and energy security.
Challenges and Future Opportunities
While the outlook is promising, several challenges require strategic attention. Infrastructure for storage, transportation, and large-scale distribution remains under development. Establishing extensive networks requires coordinated planning, investment, and long-term regulatory support. Without cohesive frameworks, expansion efforts may face inefficiencies or delays.
Moreover, production costs remain influenced by the availability and pricing of renewable power. Ensuring abundant green electricity sources is essential to maintain the sustainability and affordability of hydrogen production. As renewable energy systems grow and technologies advance, these cost-related barriers are expected to lessen.
Despite these challenges, opportunities remain abundant. Emerging technologies such as advanced electrolysis methods, hybrid renewable systems, and innovative hydrogen carriers are gaining momentum. Global collaborations and trade agreements are shaping an international hydrogen economy, promoting shared knowledge, standardization, and cross-border supply chains.
The future trajectory of the green hydrogen sector aligns with broader environmental commitments and corporate sustainability frameworks. As markets increasingly demand low-carbon solutions, green hydrogen is poised to become a cornerstone of the global clean-energy transition. Its versatility, scalability, and alignment with long-term climate objectives underscore its importance in creating a resilient and sustainable energy system for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What makes green hydrogen different from other forms of hydrogen?
Green hydrogen is produced using renewable electricity, making it a clean option compared to alternatives created through fossil-based processes.
Q: Which industries benefit the most from green hydrogen adoption?
Industries such as transportation, chemicals, steel, and energy storage benefit significantly due to hydrogen’s high energy density and clean performance.
Q: What are the major obstacles to expanding green hydrogen infrastructure?
Key challenges include developing large-scale storage and transport networks, ensuring stable renewable power supply, and reducing production costs.
More Related Reports